Metal fabrication is a critical process that plays a pivotal role in the manufacturing and construction industries. It involves the creation of metal structures by cutting, bending, and assembling processes tailored to meet specific project requirements. Successful metal fabrication is not merely about technical skill; it also requires careful planning, an understanding of materials, and adherence to safety protocols. As projects become increasingly complex, mastering the art of metal fabrication is essential for achieving efficiency and precision in your work.
To navigate the challenges associated with metal fabrication, having a solid foundation of best practices can lead to remarkable outcomes. By implementing key strategies, project managers and fabricators alike can enhance their workflow, reduce costs, and ensure high-quality results. This guide aims to provide you with ten indispensable tips that will streamline your metal fabrication processes, help you avoid common pitfalls, and ultimately drive the success of your projects. Whether you are a seasoned professional or just starting in the field, these insights will serve as a valuable resource in refining your approach to metal fabrication.

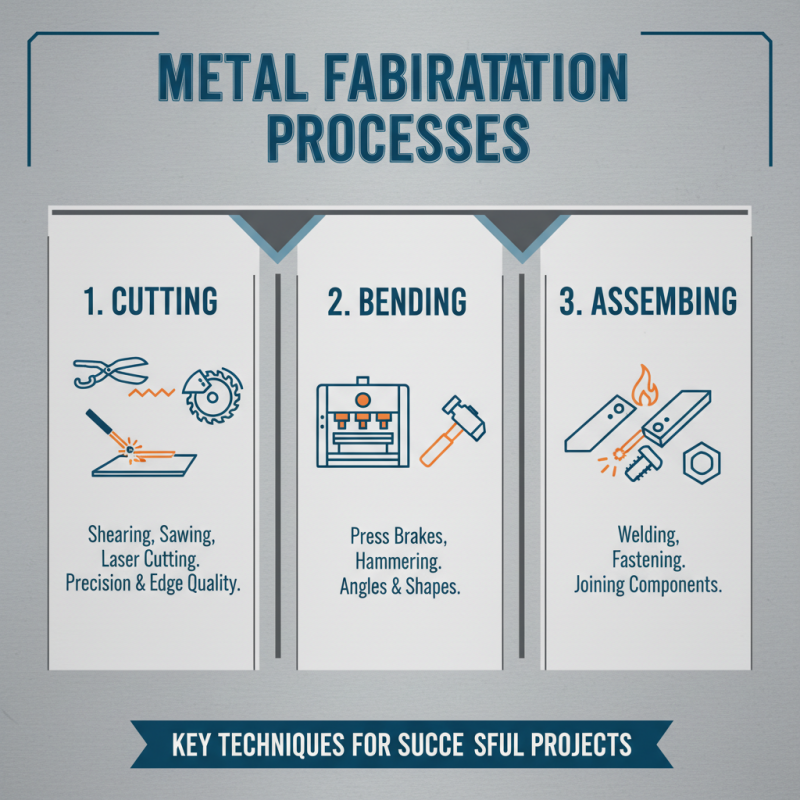
Metal fabrication is a complex process that involves various techniques designed to manipulate metal into a desired shape or form. Understanding these processes is crucial for anyone looking to achieve successful outcomes in their projects. The primary methods of metal fabrication include cutting, bending, and assembling, each serving a specific purpose in shaping the final product. Cutting can be executed through various means, such as shearing, sawing, or laser cutting, depending on the precision and edge quality required. Bending processes, on the other hand, involve deforming the metal sheets using techniques like press brakes or hammering, allowing for the creation of intricate angles and forms.
In addition to basic techniques, familiarity with welding and finishing methods is essential for a comprehensive understanding of metal fabrication. Welding is the process of joining two or more pieces of metal through the application of heat or pressure, making it foundational for assembling structures that require strength and durability. After the primary fabrication processes, finishing techniques such as grinding, painting, or coating are employed to protect the metal and enhance its aesthetic appeal. Having a clear grasp of these processes and techniques not only ensures accuracy and quality but also equips fabricators to troubleshoot and innovate, significantly impacting the success of their projects.
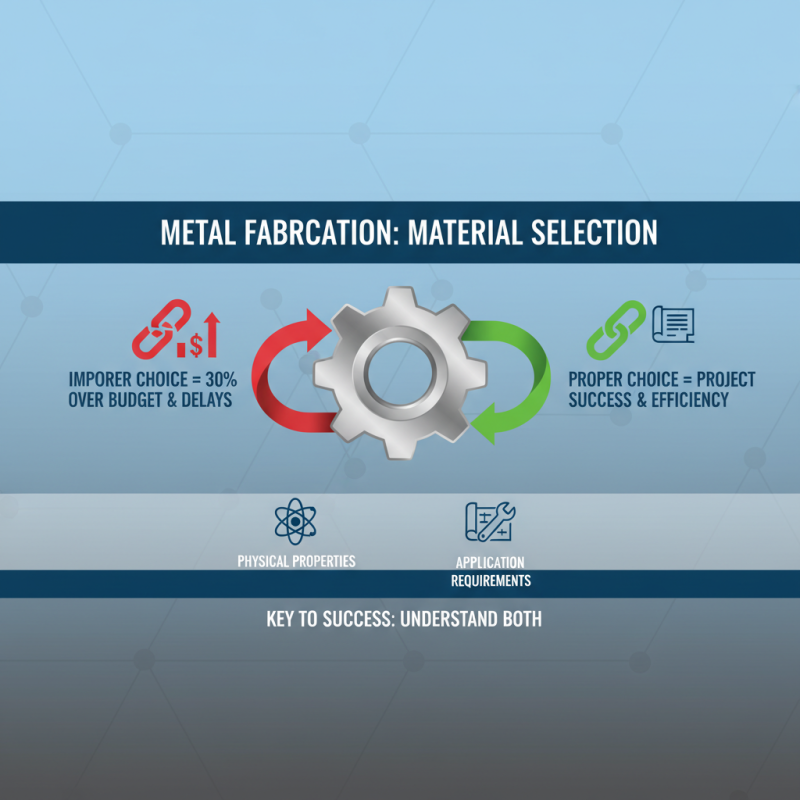
In metal fabrication, the selection of materials plays a pivotal role in determining the ultimate success of a project. Industry reports indicate that improper material choices can lead to significant increases in production costs and project delays. For instance, a study by the Fabricators & Manufacturers Association highlighted that nearly 30% of fabrication projects exceed budget due to suboptimal material selection. This underscores the necessity of a thorough understanding of both the physical properties of metals and the specific requirements of the intended application.
Choosing the right material not only affects durability and strength but also influences factors like corrosion resistance and ease of machining. According to a report from the American Institute of Steel Construction, utilizing high-strength alloys can reduce the overall weight of structures, leading to savings in transportation and handling costs. Additionally, selecting materials tailored to the project’s environmental conditions—such as stainless steel for projects subjected to harsh weather—can ensure longevity and performance. Fabricators who prioritize material selection are more likely to achieve efficiency and cost-effectiveness, ultimately contributing to a more successful fabrication process.
Quality control is a critical aspect of metal fabrication, as it directly influences the precision and reliability of the final product. Implementing systematic inspection protocols throughout the fabrication process ensures that all components meet defined specifications. This begins with selecting the right materials and extends through every stage of production, including cutting, welding, and finishing. Regular checks at each phase can catch inconsistencies early, reducing the risk of faults in the finished item.
Another vital element in quality control is the use of advanced measurement tools and techniques. Utilizing technologies such as laser scanning or coordinate measuring machines allows for highly accurate assessments of dimensions and tolerances. These measurements can identify deviations that are not visible to the naked eye, enabling quick adjustments to minimize waste and rework. Additionally, fostering a culture of quality within the workforce is essential; training employees on best practices and the importance of precision can further enhance the overall effectiveness of quality control measures, leading to improved end results in metal fabrication projects.
Welding and joining techniques are critical components in any metal fabrication project. According to the American Welding Society (AWS), approximately 20% of all manufacturing jobs require some form of welding, highlighting the necessity for proficiency in these methods. A well-executed weld not only enhances the structural integrity of the final product but also minimizes the risk of defects that can lead to costly repairs. To achieve high-quality welds, fabricators should focus on technique, material compatibility, and environmental conditions. Proper joint design and fit-up can also significantly influence the quality of the weld, as gaps and misalignments can lead to weaknesses.
Moreover, the choice of welding method greatly impacts the outcome of the project. A report from the International Institute of Welding (IIW) indicates that 85% of disputes concerning weld quality arise from improper technique or insufficient preparation. Therefore, fabricators must consider various factors, including the types of metals being joined, the thickness of materials, and the intended application of the assembled parts. Additionally, implementing best practices such as preheating, using the right filler material, and controlling the heat input can prevent issues like warping and cracking—common challenges in metal fabrication. Prioritizing these elements ensures not only effective welding but also a successful project outcome.
In the realm of metal fabrication, advanced machinery and technology play a pivotal role in enhancing productivity and precision. Tools like CNC machines and laser cutters have revolutionized the industry, allowing fabricators to achieve intricate designs and tight tolerances that manual methods simply cannot match. These technologies not only improve the quality of the final product but also significantly reduce production time and material waste, leading to more efficient workflows.
To maximize the benefits of modern machinery, one essential tip is to invest in training for your team. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of advanced tools ensures that operators can harness their full potential, reducing errors and enhancing overall production quality. Additionally, regular maintenance of equipment can greatly decrease downtime and prolong the lifespan of machinery.
Embracing automation is another crucial aspect of modern metal fabrication. By integrating automated processes, fabricators can streamline operations and increase output. Such systems can handle repetitive tasks, leaving skilled workers free to focus on more complex aspects of a project. This synergy between cutting-edge technology and skilled craftsmanship is vital for achieving success in today's competitive landscape.