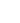Mastering carbon steel casting techniques is crucial for achieving high-quality results in metalworking. Industry expert John Smith states, "The key to success in carbon steel casting lies in understanding the material’s properties." This insight reflects the importance of skill and knowledge in this trade.
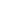
Carbon steel casting involves complex processes. It requires an understanding of temperature control and proper mold design. Precision is vital, and even small errors can lead to significant defects. For instance, inconsistent heating can cause cracks. Therefore, attention to detail is essential for successful outcomes.
While mastering these techniques, practitioners often face challenges. It can be easy to overlook small adjustments in the process. These oversights can lead to undesirable results. Reflecting on these experiences helps to improve skills. Continuous learning is a fundamental part of mastering carbon steel casting.

Understanding carbon steel casting is crucial for producing high-quality components. The process begins with selecting the right type of carbon steel. This choice impacts the final properties of the cast object. For instance, lower carbon content offers higher ductility but lower strength. Conversely, higher carbon content enhances hardness but reduces flexibility.
Molding techniques play an essential role in the casting process. Traditional sand molds are often preferred due to their cost-effectiveness. However, they may not produce the desired surface finish. Alternatives, like investment casting, offer finer details but can be significantly more expensive. One must also consider cooling rates. Uneven cooling can lead to defects like warping or cracking, which is a frequent challenge in carbon steel casting.
Post-casting processes like machining and heat treatment are often necessary to achieve specific properties. Yet, these steps can introduce new risks, such as residual stresses. Every foundry faces unique challenges, and reflecting on past mistakes can provide valuable insights. Continuous learning in carbon steel casting is key to mastering its intricacies.
Creating high-quality carbon steel castings requires the right tools and equipment. Essential items include a furnace, crucibles, and molds. A reliable furnace can reach high temperatures needed for melting steel. Crucibles come in various materials, but choosing one with high thermal stability is crucial. Molds should be designed to withstand the heat and pressure during casting.
Investing in safety gear is non-negotiable. Heat-resistant gloves protect your hands from burns. Safety goggles shield your eyes from sparks and debris. Proper ventilation is also important as fumes can be harmful. It’s easy to overlook safety, but a small mishap can derail your entire project.
Tips: Always check your equipment before starting an operation. Regular maintenance can prevent unexpected failures. Document your casting processes. This practice helps you improve over time and avoid repeating mistakes. Reflect on each casting batch. Understand what worked well and what didn’t. Embrace the learning curve; every failure leads to improvement.
| Technique | Description | Essential Tools | Safety Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | A process where sand is used to create a mold for molten steel. | Molding sand, patterns, pouring tools | Face shields, gloves, respiratory protection |
| Investment Casting | A precise casting method using a wax pattern covered in a ceramic shell. | Wax patterns, ceramic materials, melting furnace | Heat-resistant gloves, goggles |
| Die Casting | Involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. | Die casting machine, molds | Protective clothing, face protection |
| Continuous Casting | A process that produces metal shapes by continuously pouring molten steel into a mold. | Continuous casting machine, cooling system | Safety goggles, work gloves |
| Lost Foam Casting | A method where a foam pattern is used and lost during the casting process. | Foam patterns, sand for mold | Respirator, heat-protective gear |

When preparing molds for carbon steel casting, attention to detail is essential. The process often begins with selecting the right materials for the mold. Typically, sand is favored due to its excellent thermal properties. An industry report by the International Journal of Metalcasting notes that up to 70% of foundries utilize sand molds for their versatility and cost-effectiveness. This choice aids in achieving precise mold shapes, ensuring high-quality casts.
Tips: Ensure your sand mixture retains moisture but is not overly wet. Properly balanced moisture enhances mold strength and prevents defects. Common defects include surface imperfections and misalignment, which can be minimized by adjusting moisture levels.
After preparing your mold, it's crucial to inspect it thoroughly. Tiny cracks or inconsistencies can lead to catastrophic casting failures. According to research, around 30% of casting defects are linked to mold quality. Therefore, applying a consistent coating of release agent can help in removing the casting without damaging the mold.
Tips: Use a thin layer of release agent. A thick application may alter mold dimensions. This approach can help avoid unwanted surprises during the casting process, leading to a smoother workflow.
Carbon steel casting poses several challenges that can test even seasoned professionals. One common issue is achieving uniform temperature control. If the metal cools unevenly, it can lead to defects like shrinkage or warping. Maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the mold helps create a more reliable cast. Using thermal blankets or adjusting furnace settings can make a significant difference.
Another challenge is the tendency for inclusions in the final product. These unwanted particles can weaken the overall structure. Properly preparing materials and keeping a clean workspace is crucial. Regular inspection of raw materials can prevent contaminants from being introduced into the mix. Proper filtering of the molten metal can minimize these issues as well.
Lastly, it's essential to recognize the intricacies of mold design. A poorly designed mold can lead to problems like misalignment or excessive finishing work. Engaging in a thorough design and review process is vital. While these challenges can be daunting, acknowledging them is the first step in overcoming them effectively. Mistakes can happen, and reflection often leads to improvement in casting techniques.
Finishing and quality control are crucial in steel casting. These practices ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. Proper surface treatments can significantly enhance the durability of castings. Techniques like shot blasting and polishing should be considered. Each method offers a different finish, impacting the casting's appearance and performance.
Quality control starts with inspection during the casting process. Visual checks for defects are essential. However, not every flaw is visible to the naked eye. Advanced techniques like X-ray and ultrasonic testing can reveal internal issues. Regular audits and checks can help identify recurring problems. Reflections on these flaws are vital for improving casting quality.
Maintaining a clean work environment can reduce contaminants. Dust and foreign materials can degrade the final product. There’s always room for improvement in processes. Gathering feedback from the team can highlight areas needing attention. Each step matters, and overlooking minor details can lead to significant issues. It’s a journey of learning and adapting to achieve excellence.