In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, mastering metal fabrication techniques is essential for achieving high-quality results in various projects. According to a recent report by Research and Markets, the global metal fabrication market is projected to reach $10.26 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for skilled professionals in this field. Metal fabrication encompasses a range of processes, including cutting, welding, and machining, which are crucial for producing everything from intricate machinery parts to large structural components. As industries strive for efficiency and innovation, understanding the nuances of metal fabrication not only enhances project outcomes but also contributes to a more sustainable manufacturing ecosystem. This guide will equip you with the essential techniques and knowledge required to excel in metal fabrication, ensuring your projects stand out in a competitive market.
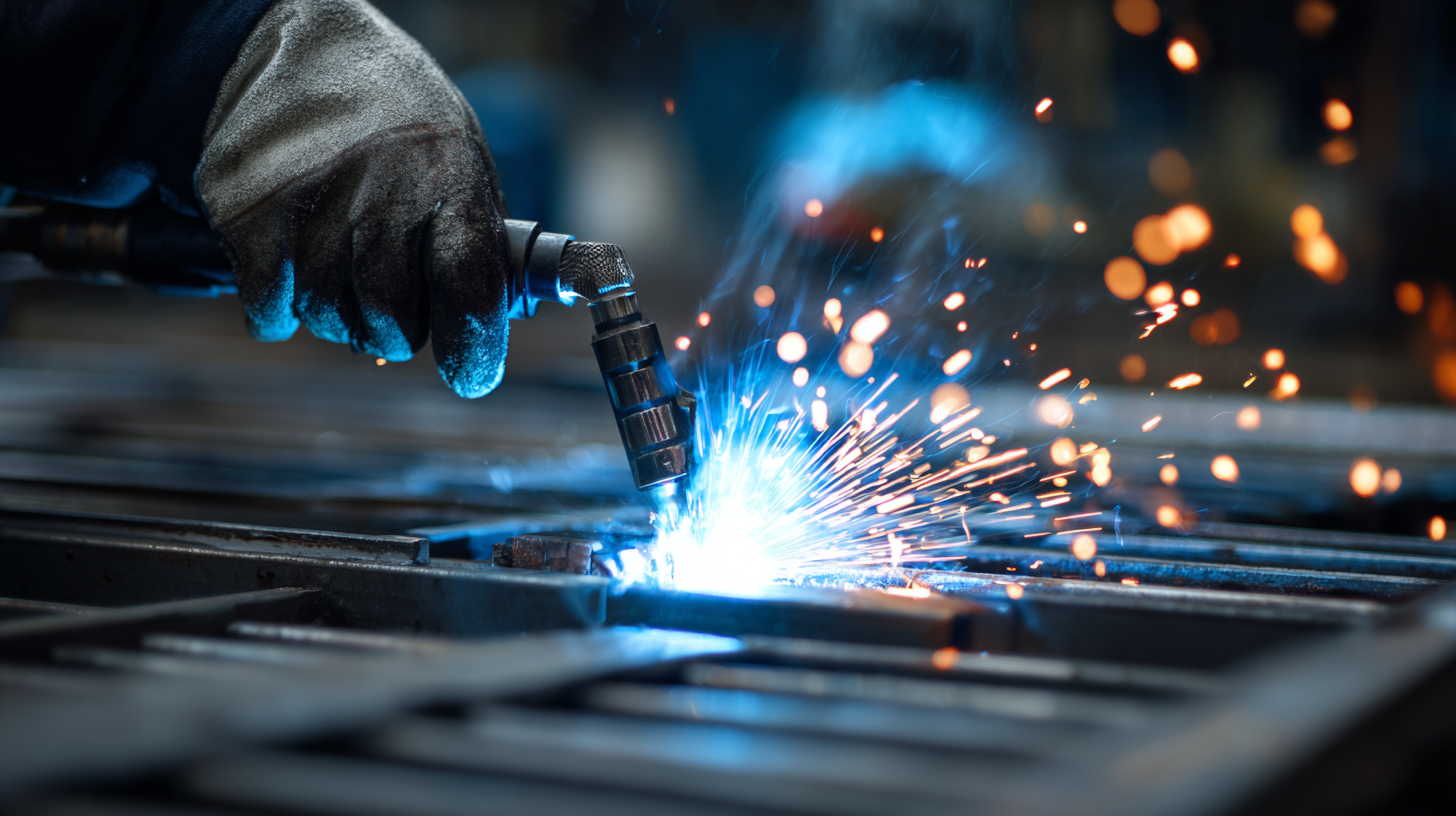

Metal fabrication is a crucial discipline in various industries, and understanding its foundational processes can significantly enhance a beginner's skills. According to a report by IBISWorld, the metal fabrication industry is expected to grow at an annual rate of 2.5% over the next five years, indicating a strong demand for skilled professionals. At its core, metal fabrication involves several processes, such as cutting, bending, and assembling metal structures. Beginners should focus on mastering these basics, as they form the bedrock of more complex techniques.
One essential process to grasp is welding, which accounted for nearly 32% of the industry’s total revenue in 2022, based on the Fabricators & Manufacturers Association’s (FMA) findings. Familiarity with various welding techniques, like MIG and TIG, can significantly improve the quality and durability of fabricated parts. Additionally, understanding materials is vital; for instance, aluminum and stainless steel are commonly used due to their favorable properties, such as resistance to corrosion and high strength-to-weight ratios. As beginners delve into these processes, they position themselves to tackle increasingly sophisticated fabrication projects with confidence.
When embarking on a journey to master metal fabrication techniques, arming yourself with the right tools and equipment is crucial. According to the 2021 Fabricators & Manufacturers Association (FMA) data, nearly 60% of industry professionals indicate that having high-quality tools significantly enhances the precision and efficiency of their projects. Key tools such as MIG and TIG welders, plasma cutters, and metal bending machines are essential for any fabricator. These tools not only aid in achieving cleaner cuts and stronger welds but also reduce the time spent on each project.
Tips: Invest in a reliable welding helmet that offers auto-darkening features for enhanced safety and visibility. It's also wise to familiarize yourself with various welding techniques, as each method offers unique benefits that can be applied to different types of metal and specific projects.
Additionally, the importance of a well-equipped workspace cannot be overstated. A dedicated metal shop should have proper storage for tools, high-quality workbenches, along with essential safety equipment like gloves and goggles. According to the National Association of Manufacturers, 70% of metal fabrication workers report that effective organization of tools directly correlates to reduced workplace accidents and improved productivity. Adapting your workspace with these considerations will undoubtedly elevate your metal fabrication capabilities.
Mastering metal fabrication techniques is essential for any DIY enthusiast or professional. A precise methodology in cutting and shaping metal is critical to ensure accuracy and quality in your projects. According to a report by the Fabricators & Manufacturers Association, 74% of manufacturers consider precision in metal fabrication a crucial aspect of their workflow, directly impacting product durability and performance.
When it comes to cutting metal, select the right tools for the material type. Plasma cutters, saws, and shears each serve specific purposes. For instance, plasma cutting is ideal for thick materials, providing clean edges with minimal time required. Always use proper safety gear and ensure your workspace is well-ventilated.
Tips: Always double-check your measurements before cutting. A small error can lead to significant material wastage. Additionally, when shaping metal, consider the use of jigs or fixtures to maintain consistency across multiple pieces.
Shaping metal accurately involves techniques like bending, welding, or machining. Understanding the metal’s properties, such as tensile strength and ductility, is necessary for successful manipulation. A recent industry report highlighted that 68% of metal fabricators face challenges in delivering consistent product specifications due to insufficient knowledge of the material's behavior under various conditions. Emphasizing training in these areas can lead to fewer reworks and enhanced efficiency.

Mastering metal fabrication techniques is essential for any DIY enthusiast or professional fabricator. One of the cornerstones of this craft is understanding the various methods for joining metals. Welding and soldering are two vital techniques, each serving different purposes depending on the materials and desired results.
Welding is a popular method for joining metals, as it creates a strong, permanent bond through the melting and fusing of base metals. This technique is commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as structural steelworks. When welding, always ensure proper shielding is in place to prevent contamination. **Tip:** Invest in quality protective gear and practice welding on scrap metal to refine your skills before tackling major projects.
Soldering, on the other hand, is generally used for joining metal components at lower temperatures. This technique is ideal for electronics and plumbing projects, where a high degree of precision is required. **Tip:** Clean the surfaces before soldering to remove any oxides or dirt, as this will ensure a better connection. Additionally, using a flux can help improve the flow of the solder, resulting in a stronger joint. By mastering these joining techniques, you will enhance the quality and durability of your metal projects.
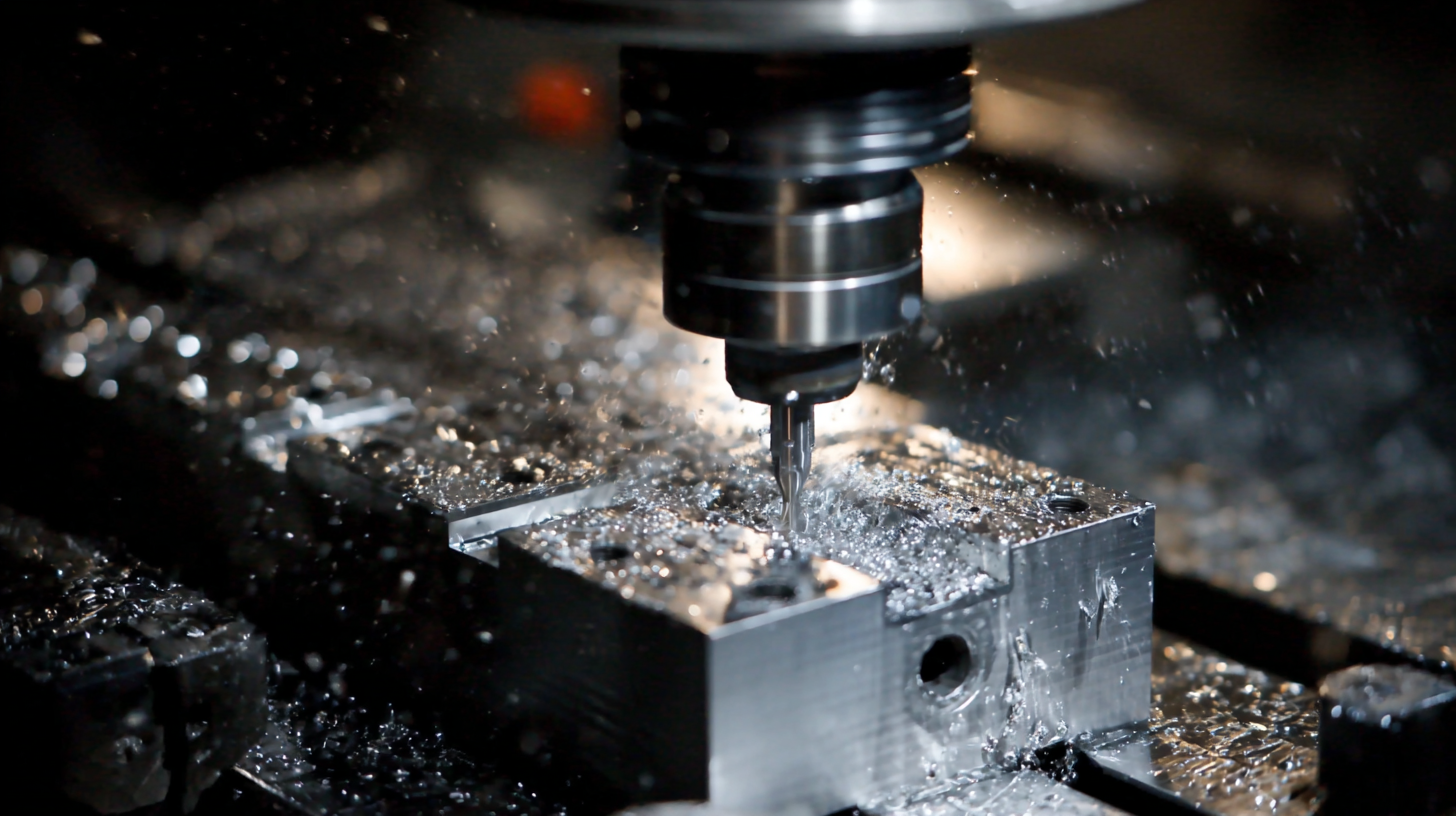

When engaging in metal fabrication, adhering to safety practices is paramount to protect yourself and those around you. First and foremost, always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses, gloves, and a welding helmet if you're working with welding equipment. These items shield you from harmful debris, intense light, and heat. Additionally, ensure your clothing is made from flame-resistant materials to minimize the risk of burns. It’s essential to maintain a tidy workspace to prevent accidents caused by clutter or misplaced tools.
Moreover, understanding the tools you are using is crucial. Always read and follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper use and maintenance of your equipment. Before starting any project, inspect your tools for signs of damage and ensure safety guards are in place. When operating machines like saws or welding equipment, keep your hands and other body parts clear of moving parts to avoid injury. Lastly, maintain good ventilation in your workspace to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. By prioritizing these safety practices, you can create an environment conducive to effective and secure metal fabrication.