Metal fabrication is a vital process in various industries, serving as the backbone for creating everything from household appliances to complex machinery. As technology advances and the demand for custom solutions increases, understanding the techniques and applications of metal fabrication becomes essential for both beginners and seasoned professionals. This guide aims to demystify the often intricate world of metal fabrication, providing clear insights into fundamental methods such as welding, machining, and cutting, as well as exploring their practical applications in real-world scenarios. By unlocking the secrets of metal fabrication, readers can gain valuable knowledge that will empower them to tackle projects confidently, whether they're hobbyists or aspiring craftsmen. This journey into metal fabrication not only enhances technical skills but also fosters creativity and innovation in designing and producing metal components.
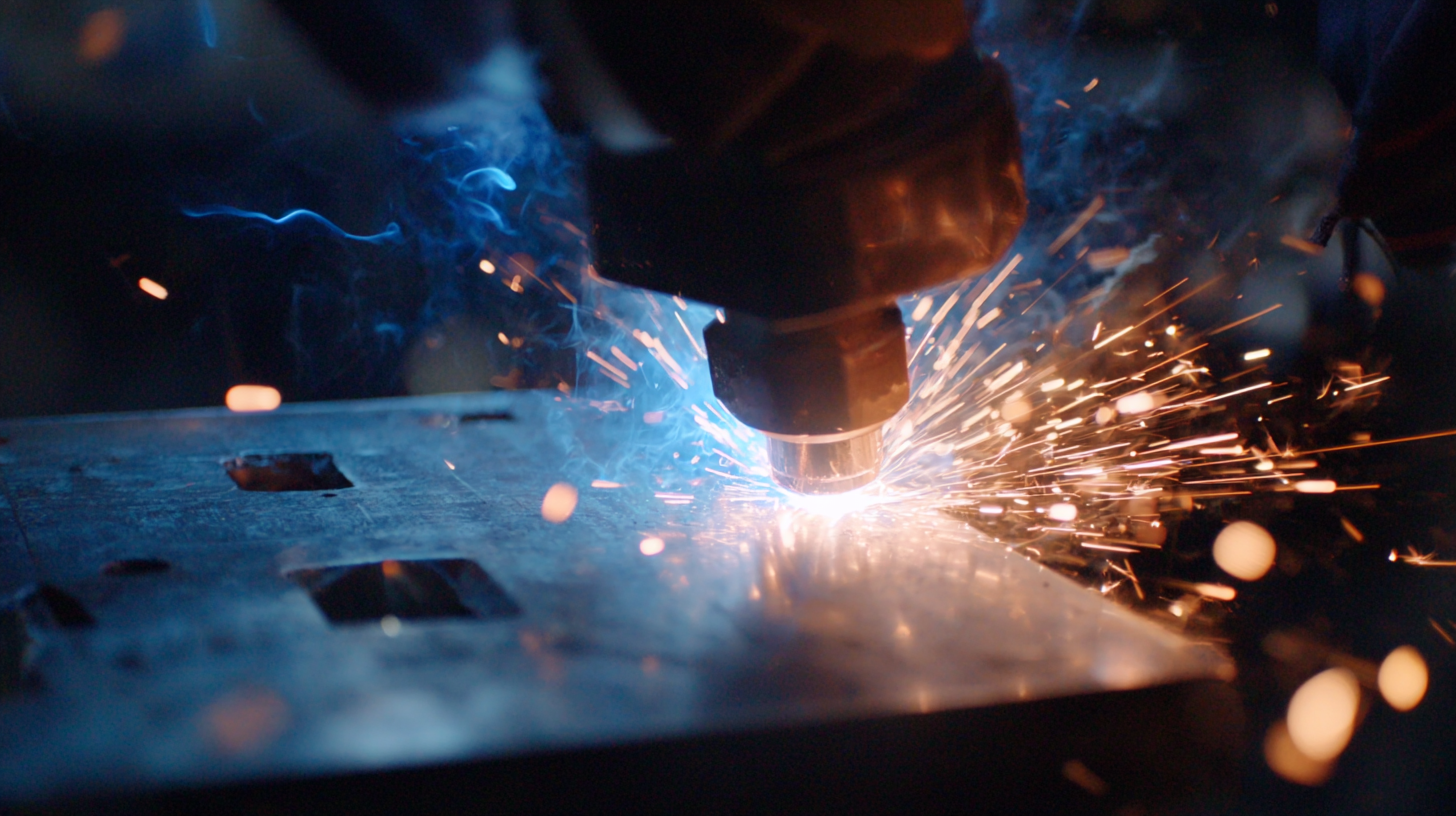

Metal fabrication is an essential process in various industries, encompassing a range of techniques that transform raw materials into functional structures. Understanding the fundamentals of metal fabrication involves familiarizing oneself with key processes such as welding, cutting, bending, and machining. Each technique serves a distinct purpose; for instance, welding joins metal pieces together, while cutting can create precise shapes from larger sheets of material. These foundational skills are crucial for anyone looking to enter the field or enhance their existing knowledge.
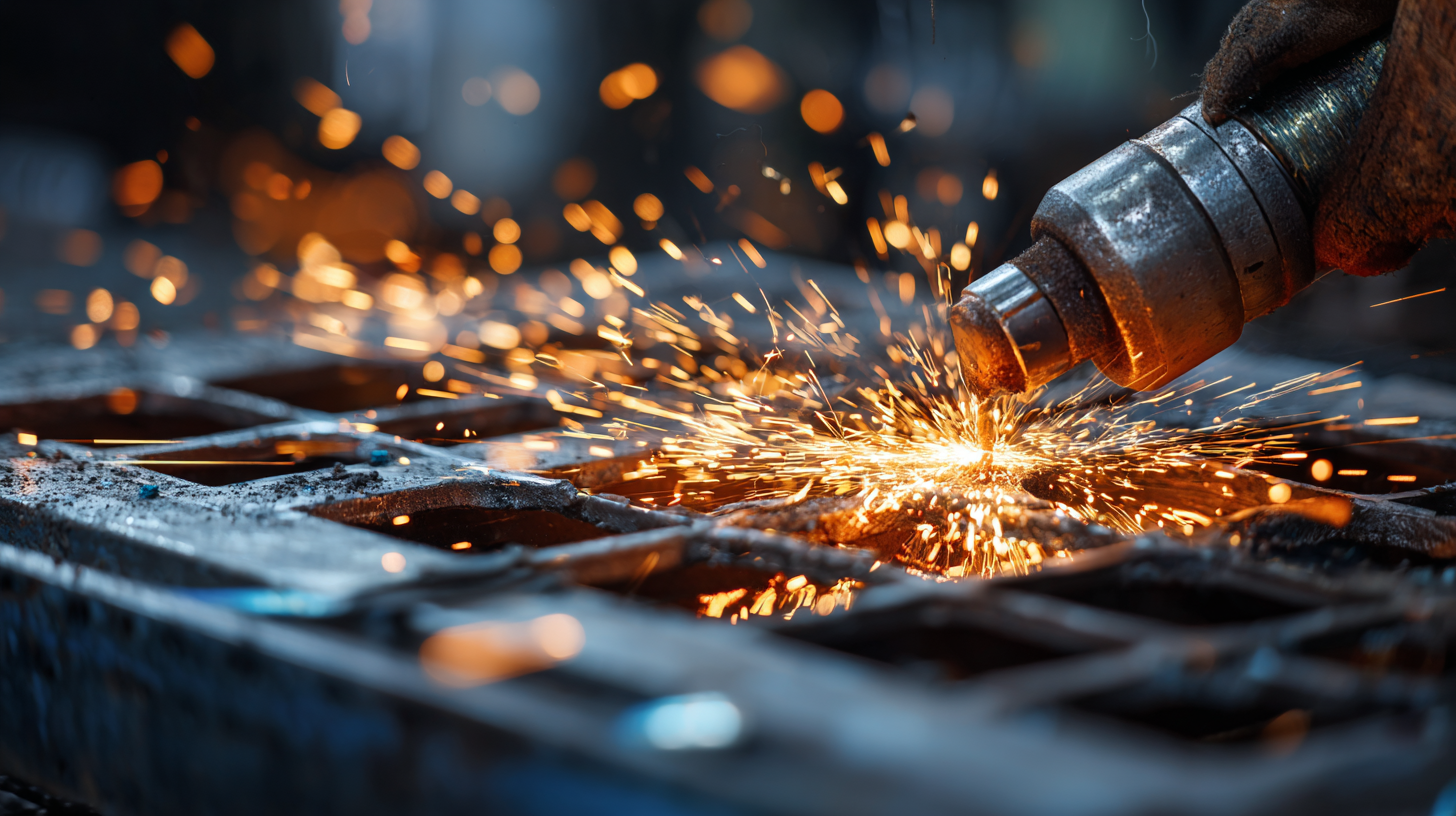

In addition to the basic techniques, it's important to recognize the applications of metal fabrication across diverse sectors. From manufacturing components for automobiles to crafting intricate designs for architecture, fabricated metal plays a pivotal role in both functionality and aesthetics. This versatility highlights the significance of mastering various metalworking techniques, enabling professionals to tailor solutions that meet specific project requirements. By understanding these fundamentals, beginners can develop a strong foundation for further exploration and advancement in the world of metal fabrication.
When embarking on metal fabrication projects, having the right tools and equipment is crucial for beginners. Essential tools include a welding machine, which allows for the joining of metal pieces through heat, and a cutting tool, such as a plasma cutter or metal saw, to shape materials accurately. A bench grinder is also important for smoothing edges and finishing cuts, ensuring that the metal surfaces are safe and ready for assembly.
In addition to these primary tools, safety equipment cannot be overlooked. A proper welding helmet protects against harmful sparks and UV radiation, while gloves safeguard hands from sharp metal edges and heat. Clamping tools and jigs can help stabilize workpieces, allowing for more precise and efficient assembly. By investing in these fundamental tools and emphasizing safety, beginners can confidently explore the world of metal fabrication and develop their skills through hands-on experience.
Welding is an essential skill for various applications, including agricultural repairs, automotive industries, and even home projects. For beginners, mastering basic welding techniques is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness in their work. Fundamental techniques such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, and stick welding each serve different purposes and materials. According to recent industry reports, over 50% of farms in the U.S. rely on welding for essential repairs, highlighting the significance of these skills in agricultural settings.
Safety is paramount in welding, regardless of the application. New welders should familiarize themselves with safety gear, including helmets, gloves, and protective clothing to prevent burns and injuries. Additionally, understanding the workspace environment, ventilation, and potential hazards is essential. Industry experts recommend that beginners engage in training programs or workshops that offer hands-on experience, as practical knowledge significantly enhances learning outcomes. As technology advances, integrating smart technology and automation into welding processes presents exciting opportunities for efficiency and precision, reshaping the future landscape of this vital industry.
| Technique | Description | Applications | Safety Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIG Welding | A welding process that uses a continuously fed wire electrode and an inert gas to protect the weld pool. | Automotive repairs, construction, and fabrication of metal structures. | Use proper ventilation, wear protective gear, and avoid exposure to fumes. |
| TIG Welding | A precise Welding method that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and requires a filler rod. | Aerospace components, thin materials, and critical welds requiring high quality. | Maintain a safe distance from the arc, use protective clothing, and ensure a clean workspace. |
| Stick Welding | Uses a rod coated in flux to create the weld and can be used for all positions. | Construction, maintenance, and repair of heavy equipment and structural steel. | Wear a welding helmet and protective gloves to shield against sparks and UV radiation. |
| Plasma Cutting | A process that cuts through electrically conductive materials by means of an accelerated jet of hot plasma. | Metal fabrication, art projects, and automotive industry. | Use protective eyewear and ensure adequate ventilation to avoid inhalation of harmful fumes. |
Metal fabrication plays a pivotal role in various industries, each harnessing its techniques to improve efficiency and productivity. In the automotive sector, for instance, metal fabrication is crucial for manufacturing components that are lightweight yet durable, enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Techniques such as cutting and welding enable the creation of complex shapes, ensuring that parts meet the stringent safety and functionality standards required in modern vehicles.

Similarly, the aerospace industry relies heavily on advanced fabrication methods to produce high-performance parts that must withstand extreme conditions. Metal fabrication techniques are employed to create intricate components for aircraft, which are vital for safety and reliability. The use of specialized equipment, such as machining and welding tools, allows for the precise manufacturing of these critical parts, underscoring the importance of metal fabrication across various applications.
As industries evolve, the continuous exploration of new technologies and techniques in metal fabrication will drive innovation and propel growth in these sectors.
Metal fabrication is a complex process that often comes with its own set of challenges. One common issue faced by beginners is the difficulty in selecting the right materials for specific projects. It's essential to understand the properties of metals, such as strength, malleability, and corrosion resistance, to prevent project failures. To overcome this, beginners should conduct thorough research and consult with experienced fabricators to ensure they are choosing the appropriate materials that align with the project requirements and intended use.
Another frequent challenge in metal fabrication is achieving precise cuts and measurements. Inaccuracies can lead to wasted materials and time, causing frustration for novices. Investing in quality tools and machinery, alongside practicing proper measurement techniques, can significantly improve accuracy. Additionally, using computer-aided design (CAD) software can help visualize designs and ensure all dimensions are correctly accounted for before actual fabrication begins, leading to a more successful and efficient workflow.