In the contemporary landscape of industry and innovation, Metal Manufacturing stands as a cornerstone that fuels technological advancements and economic growth. This essential sector not only provides the raw materials necessary for a wide range of applications, but it also drives the development of new technologies and solutions across various fields. From automotive and aerospace to construction and energy, the role of metal manufacturing in producing durable and reliable components is undeniable.
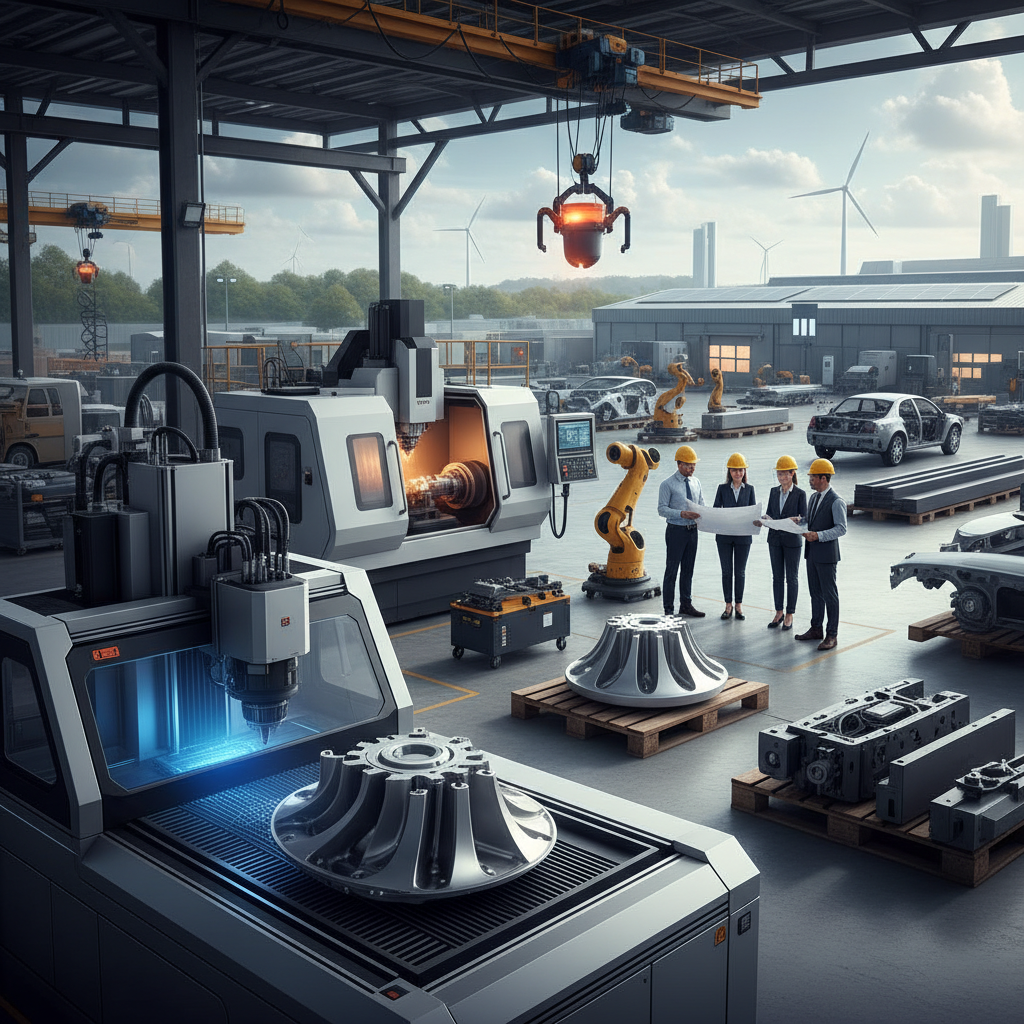

As industries face the challenges of modern demands, particularly in sustainability and efficiency, Metal Manufacturing evolves to meet these needs through innovative processes and materials. Incorporating cutting-edge techniques such as additive manufacturing, precision machining, and advanced alloy development enables manufacturers to create lighter, stronger, and more complex products. This evolution is critical for businesses aiming to enhance performance while reducing environmental impact.
The significance of Metal Manufacturing extends beyond mere production; it influences the entire supply chain, fosters job creation, and paves the way for future innovations. As we delve deeper into the integral role of Metal Manufacturing, we will explore its contributions to modern industry and the innovations that emerge as a result of this vital sector.
The historical significance of metal manufacturing in industry can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where the ability to mold and shape metals marked a turning point in technological advancement. Early metalwork laid the foundation for tools, weapons, and structures, enabling societies to thrive and expand. The ability to extract and refine metals like copper and bronze was pivotal in the development of agriculture and trade, propelling human innovation forward. This period not only signaled the dawn of metallurgy but also set the stage for social and economic transformations that would shape the course of history.
As industrialization emerged in the 18th and 19th centuries, metal manufacturing evolved further, becoming the backbone of modern industry. The introduction of iron and steel into construction and manufacturing processes revolutionized transportation and infrastructure. Factories began to utilize metal components for machinery, which in turn enhanced productivity and efficiency. The advancements made in metalworking techniques, such as casting and forging, facilitated mass production, thereby driving economic growth and enabling the establishment of complex economies. The historical trajectory of metal manufacturing illustrates its critical role in shaping modern civilization and fostering continued innovation across various sectors.

Metal manufacturing plays a critical role in modern industry, with various metals being pivotal in the development of innovative products and technologies. Among these, steel stands out due to its unmatched strength and versatility, making it a cornerstone in construction and automotive manufacturing. The addition of alloys, such as chromium and nickel, enhances its properties, enabling the production of durable structures and high-performance vehicles.
Aluminum is another key metal that significantly contributes to modern manufacturing. Its lightweight nature, combined with resistance to corrosion, makes it essential for aerospace and consumer electronics industries. Aluminum's ability to be easily shaped and recycled further underscores its importance in sustainable manufacturing practices.
Additionally, metals like copper and titanium serve specialized applications; copper is vital for electrical conductivity, while titanium's strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for medical implants and high-stress components. This diverse range of metals and their applications underscores the importance of metal manufacturing in driving technological advancements and industrial growth.
The landscape of metal manufacturing is undergoing a revolutionary transformation, driven by cutting-edge technological innovations. One of the most significant advancements is the integration of automation and robotics in the manufacturing process. Automated systems streamline production, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. These technologies not only boost output but also allow for the precise handling of intricate designs, meeting the ever-evolving demands of modern industries.
In addition to automation, advancements in additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, are reshaping the metal fabrication sector. This technology enables manufacturers to create complex geometries that were previously impossible or too costly to achieve with traditional methods. By utilizing materials more efficiently, companies can reduce waste and lower costs while simultaneously enhancing product performance.
Furthermore, innovations in materials science, such as the development of lightweight yet strong alloys, are paving the way for new applications in sectors ranging from aerospace to automotive, showcasing how technological progress is fundamental to the growth and competitiveness of metal manufacturing.

The role of metal manufacturing in sustainable practices is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone of modern industrial innovation. According to a report by the World Steel Association, the steel industry alone is responsible for approximately 7% of global greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the need for more sustainable production processes. Innovative technologies such as electric arc furnaces and the adoption of recycled materials are paving the way for drastic reductions in carbon footprints. In fact, using recycled steel can reduce energy consumption by up to 75%, demonstrating the tangible benefits of sustainable practices in metal manufacturing.
Furthermore, the integration of circular economy principles in metal manufacturing has emerged as a vital strategy for reducing waste and enhancing resource efficiency. A study by the International Institute for Environment and Development emphasizes that transitioning to a circular economy could lead to an annual savings of $1 trillion by 2025 for the global economy. By prioritizing the recycling and repurposing of metals, manufacturers can not only reduce environmental impact but also drive economic growth through sustainable innovation. This paradigm shift is essential for industries aiming to align with global sustainability goals while maintaining competitive advantages.
The future of metal manufacturing is poised for significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology and a push towards sustainability. As the industry projects growth from $653.6 billion in 2025 to $742.1 billion by 2033, with an annual growth rate of approximately 1.6%, it's clear that innovation will play a crucial role. Key trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and digital twin technologies, which enhance design simulations and facilitate precise manufacturing processes, leading to more innovative applications.
Tips: As companies embrace these technologies, investing in training for employees to effectively utilize AI tools will be essential. Additionally, exploring green innovations in materials—such as copper—can propel businesses toward meeting the demands of modern sustainability goals.
Moreover, the global demand for advanced steel and aluminum materials is shaping the future landscape. With events highlighting the latest advancements and research in these areas, manufacturers must stay agile, adapting to the latest trends in processing and product design. This forward-thinking approach will not only ensure competitiveness but also contribute to the industry's overall growth trajectory.
Tips: Attend industry conferences and workshops to stay updated on technological advancements and network with experts in the field. Emphasizing collaboration can lead to innovative solutions that drive the sector forward.
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Material Types | Steel, Aluminum, Copper, Titanium |
| Manufacturing Processes | Casting, Machining, Welding, Additive Manufacturing |
| Industry Applications | Automotive, Aerospace, Construction, Electronics |
| Emerging Technologies | 3D Printing, Robotics, IoT Integration, AI in Manufacturing |
| Sustainability Trends | Recycling of Materials, Energy Efficiency, Green Manufacturing Practices |
| Challenges | Supply Chain Disruptions, Skilled Labor Shortages, Rising Material Costs |