Steel casting is a crucial manufacturing process that involves pouring molten steel into a mold to create intricate shapes and components. This technique is widely recognized for its ability to produce durable and high-strength parts that are essential in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery. Understanding the steel casting process is vital for engineers and manufacturers alike, as it significantly influences the final product's performance and reliability.
The steel casting process encompasses several stages, from the preparation of raw materials to the cooling and finishing of casted components. Each step is meticulously designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent quality standards while optimizing material utilization. Moreover, the benefits of steel casting extend beyond just strength; it offers design flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to produce complex geometries that would be challenging to achieve through other manufacturing methods.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of steel casting, exploring its advantages, applications, and the various techniques employed in the industry. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of steel casting, readers will appreciate its significance in modern manufacturing and how it contributes to the development of reliable and innovative products.
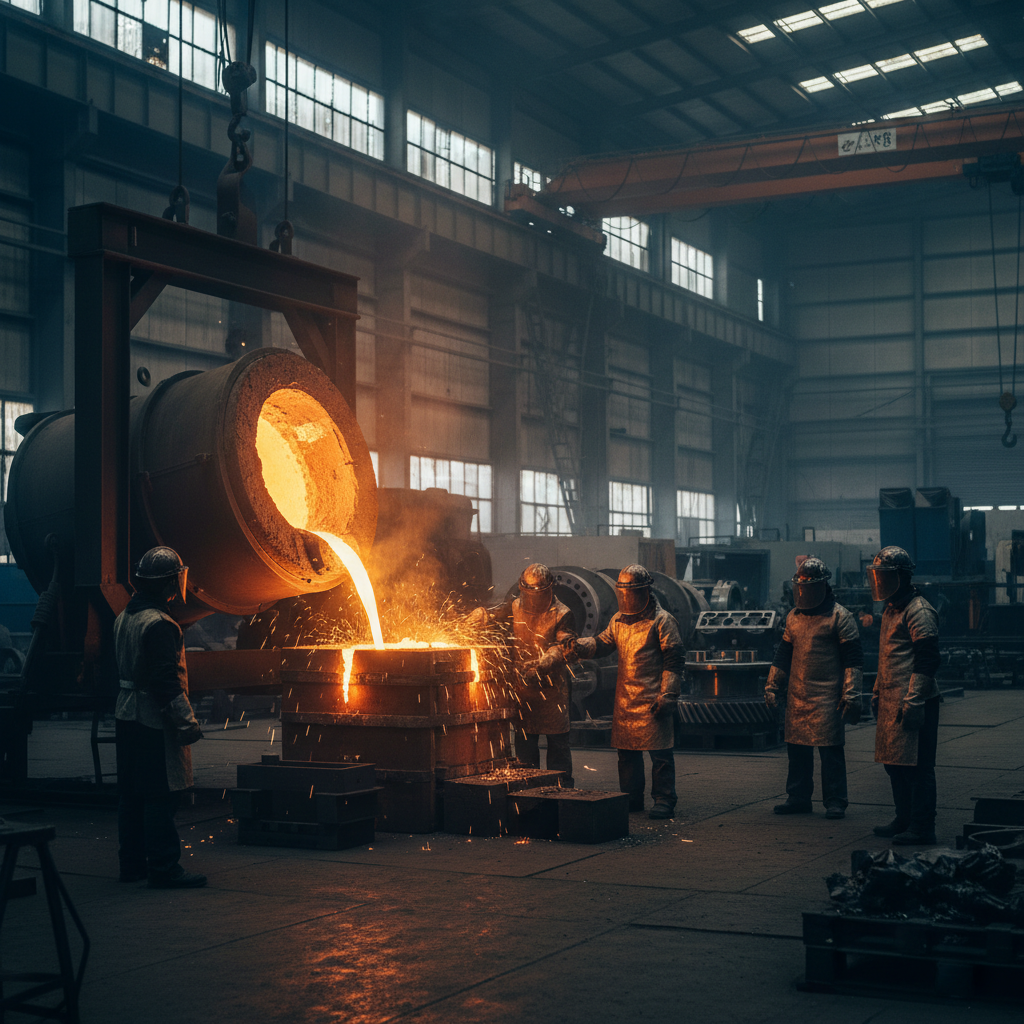

Steel casting is a critical manufacturing process that involves pouring molten steel into a mold to create components with complex shapes and precise dimensions. The materials used in steel casting typically include carbon steel, low-alloy steel, and stainless steel, each chosen for their specific properties suited to various applications. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global steel casting market is expected to reach approximately $26.3 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for steel components across multiple industries.
The steel casting process begins with the selection of raw materials, followed by melting in a furnace, where temperatures can exceed 1,600 degrees Celsius. The molten steel is then poured into molds made from sand, metal, or ceramic materials. A notable advantage of steel casting is its ability to produce large, durable components with a high degree of intricacy. A study published by Research and Markets indicates that the automotive and aerospace industries are the largest consumers of steel castings, owing to their requirements for high strength and reliability in critical components. The versatility of steel casting makes it an essential manufacturing technique in sectors ranging from construction to energy.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Steel casting is a manufacturing process where molten steel is poured into a mold to create a desired shape. |
| Materials Used | Commonly used materials include carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel. |
| Process Steps | 1. Melting - Heating steel to a liquid state. 2. Casting - Pouring into molds. 3. Cooling - Allowing the steel to solidify. 4. Finishing - Machining and surface treatment. |
| Benefits | High strength, complex shapes are achievable, durability, and cost-effectiveness for large production runs. |
| Applications | Used in automotive parts, machinery, aerospace components, and construction materials. |
| Challenges | Potential for defects, the requirement of skilled labor, and often longer lead times. |
Steel casting is a crucial manufacturing process that involves pouring molten steel into a mold to form various components. The process begins with the preparation of the steel, which can be alloyed with different elements to achieve specific properties. Once the desired composition is achieved, the steel is melted in a furnace before being poured into pre-prepared molds.
The key steps in the steel casting process include mold preparation, metal pouring, solidification, and finishing. Molds can be made from sand, metal, or ceramic, depending on the application and required precision. After pouring the molten steel into the mold, it undergoes a cooling phase, during which it solidifies and takes the shape of the mold. Once cooled, the cast piece is removed, and finishing processes such as machining and surface treatment are applied to ensure the final product meets industry standards and specifications. These techniques enable the production of complex shapes and high-strength components, making steel casting an essential technique in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and construction.
This chart illustrates the monthly production volume (in tons) of steel castings over a six-month period, highlighting the consistency and demand in various applications.
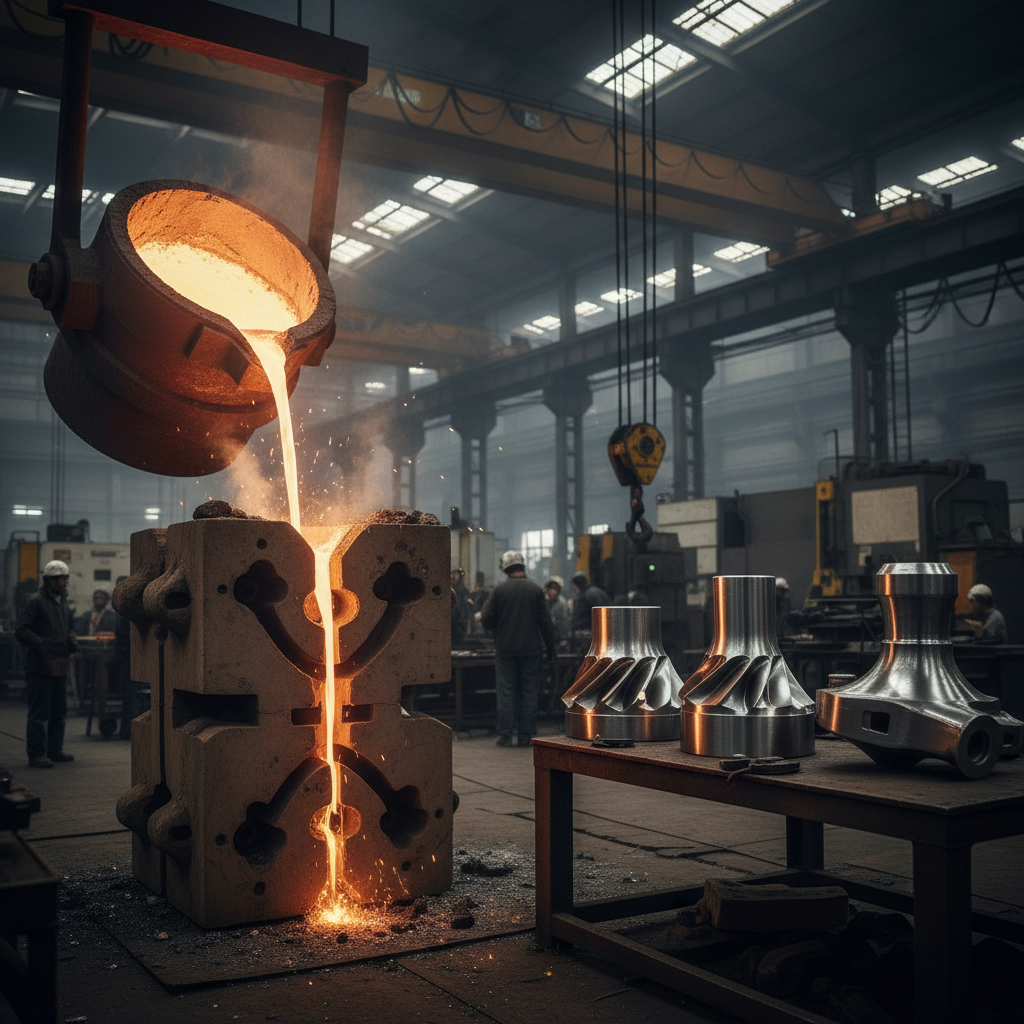

Steel casting is an essential manufacturing method known for its numerous advantages. One of the key benefits is the ability to produce complex shapes and intricate designs that are often challenging to achieve with other manufacturing processes. This capability not only enhances design flexibility but also allows for the creation of high-performance components, crucial in industries such as automotive and aerospace. The strength and durability of steel castings make them highly suitable for demanding applications, ensuring that they can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity.
In addition to design versatility, steel casting offers significant cost efficiency in mass production. The process maximizes material utilization, minimizing waste and reducing overall production costs. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as nanotechnology and smart automation, are improving the performance and energy efficiency of steel casting, making it an even more attractive option for manufacturers. The hybrid approaches like Additive Casting are further revolutionizing the field, combining the precision of 3D printing with the reliability of traditional casting methods, ultimately enhancing both the quality and efficiency of the casting process.
Steel casting plays a vital role in various industries, providing robust and versatile components essential for numerous applications. With the global steel casting market projected to reach USD 42.18 billion by 2029, the demand for steel cast products is clearly on the rise. This growth is supported by the increasing adoption of steel casting in sectors such as automotive, construction, and heavy machinery. The excellent strength-to-weight ratio and ability to create complex shapes make steel castings an ideal choice for manufacturers looking to innovate and improve product performance.
Moreover, the iron and steel casting market is expected to witness significant expansion, with projections indicating it could reach USD 254.5 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 3.8% during the forecast period from 2025. This expansion reflects the increasing reliance on steel cast components in the production of automotive parts, industrial equipment, and structural elements. Industries are capitalizing on the durability and strength provided by steel castings, underscoring their importance in advancing technology and infrastructure development across the globe.
The steel casting industry is witnessing significant innovations driven by technological advancements and environmental considerations. As manufacturers strive to enhance productivity and reduce waste, techniques like 3D printing and advanced simulation software are becoming more common. These technologies allow for the creation of complex geometries with minimal material usage, enhancing overall efficiency in the casting process.
Additionally, automation and robotics are revolutionizing production lines, leading to increased precision and reduced human error, which ultimately improves product quality.
Environmental concerns are also influencing the future of steel casting. Companies are adopting more sustainable practices, such as utilizing electric arc furnaces that lower carbon emissions compared to traditional casting methods. The push for a circular economy is encouraging the recycling of scrap metal and by-products in steel production, minimizing waste and resource consumption. As regulations tighten and consumer preference shifts toward environmentally friendly products, the steel casting industry is evolving to embrace these practices, ensuring its relevance in a more sustainable industrial landscape.