Steel fabrication is a crucial process in various industries. It involves cutting, bending, and assembling steel to create strong structures. Different techniques are utilized in steel fabrication to meet specific needs and applications. Each method has its advantages and limitations.
For instance, welding is a common technique that ensures durability. However, it requires skilled labor and safety precautions. Laser cutting offers precision but can be costly. There are also methods like plasma cutting, which is faster but may not be as accurate. Exploring these techniques unlocks their potential in various projects.
Understanding steel fabrication can lead to better decision-making. Companies often seek the best method for their unique projects. There are trade-offs involved with each technique. Recognizing these choices can impact the overall success of a project. This discourse delves into the top steel fabrication techniques and their applications. It aims at shedding light on their strengths and challenges.
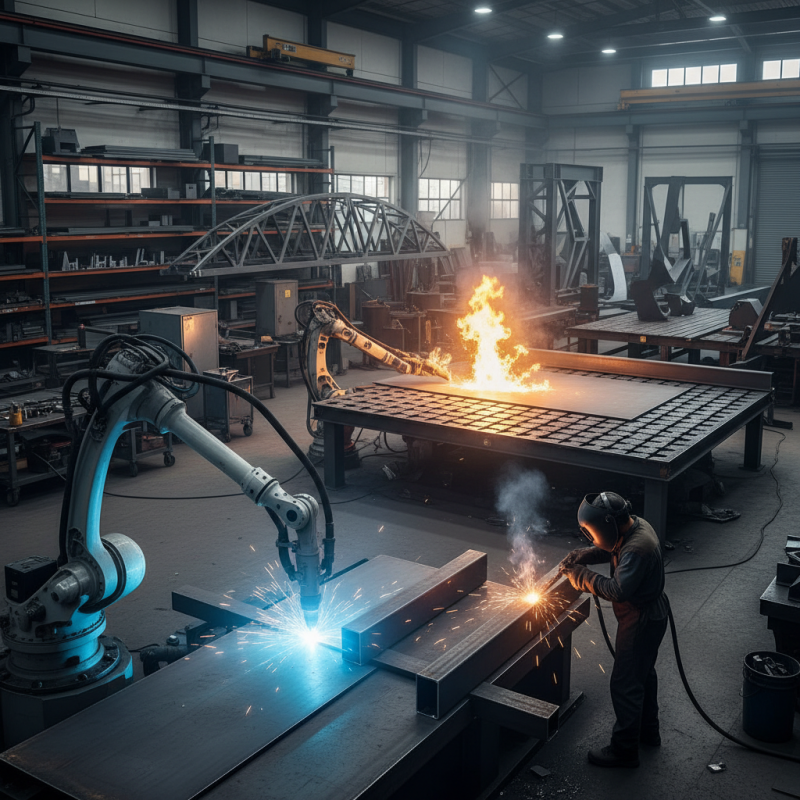

Steel fabrication is a vital process in construction and manufacturing industries. Various techniques play a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the final product. Common methods include welding, machining, cutting, and forming. Each technique offers distinct advantages depending on the project's requirements.
Welding is one of the most widely used methods, accounting for about 30% of steel fabrication processes globally. It creates strong joints and is essential for structural integrity. However, improper welding can lead to defects, which might compromise safety. Laser cutting, on the other hand, provides precise cuts with minimal material wastage. It's gaining popularity due to its efficiency.
Tips: Always inspect welded joints for cracks. Ensure proper training for operators using high-powered equipment.
Machining is another critical technique. It involves removing material to achieve desired shapes and sizes. It's best for complex parts that require tight tolerances. Despite its precision, machining can be time-consuming and costly.
Tips: Consider using computer numerical control (CNC) machines for enhanced accuracy. Regular maintenance can prevent equipment failures.
Forming techniques, like bending and rolling, manipulate material shapes without cutting it. While they can produce intricate designs, they may also introduce stresses in the material. Understanding the limitations of each technique is vital for optimal results in steel fabrication.
Welding is a crucial technique in steel fabrication. It joins metal parts together, ensuring structural integrity. Various welding methods are used, each with specific applications. For example, MIG welding is popular in industries due to its speed and versatility. It's effective for both thin and thick materials.
TIG welding, on the other hand, offers more precision. It is ideal for intricate designs and stainless steel. While it's slower, the results are often cleaner. Stick welding is another common method, often used in outdoor projects. It is less sensitive to wind and contaminants.
Different projects require different techniques. A choice depends on the materials, thickness, and location. Sometimes, the results may not meet expectations. Reflecting on these choices can lead to better decision-making in future projects. Each method has strengths and weaknesses, making the selection process challenging but essential.
| Technique | Description | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIG Welding | Metal Inert Gas welding uses a continuous wire to create a weld pool. | Automotive, manufacturing, and metalworking industries. | Fast, versatile, and suitable for thin materials. |
| TIG Welding | Tungsten Inert Gas welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to heat a workpiece. | Aerospace, artistic, and stainless steel applications. | High-quality and precise welds suitable for thinner materials. |
| Spot Welding | A technique used to join two or more metal sheets at small points using heat. | Automotive body assembly and electronics. | Quick process, ideal for high-volume production. |
| Flux-Cored Arc Welding | Similar to MIG, but uses a tubular wire filled with flux. | Construction and heavy equipment fabrication. | Effective for thick materials and outdoor conditions. |
| Oxy-Acetylene Welding | Uses a flame produced by burning acetylene with oxygen to melt metals. | Repair work and art. | Versatile and can cut or weld various metals. |
Cutting techniques are vital in steel fabrication. They ensure precision and efficiency in shaping metal. Common methods include plasma cutting, laser cutting, and water jet cutting. Each technique has unique advantages and applications.
Plasma cutting uses high-velocity jets of ionized gas. It’s fast and effective for thick materials. However, it can create rough edges. To improve the finish, consider post-cut grinding. Laser cutting, on the other hand, offers high precision. It’s best for intricate designs. But it requires careful setup to avoid distortion. Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive materials. This method is versatile and minimizes heat-affected zones. Yet, it’s often slower and more costly.
**Tips:** Always test your cutting tools on scrap material first. This prevents costly mistakes. Adjust settings based on the material thickness for better results. Regular maintenance of tools is crucial for consistent cutting quality.
This chart illustrates the various cutting techniques used in steel fabrication, showcasing their prevalence in the industry. The data reflects the percentage of usage among different methods based on recent industry surveys.
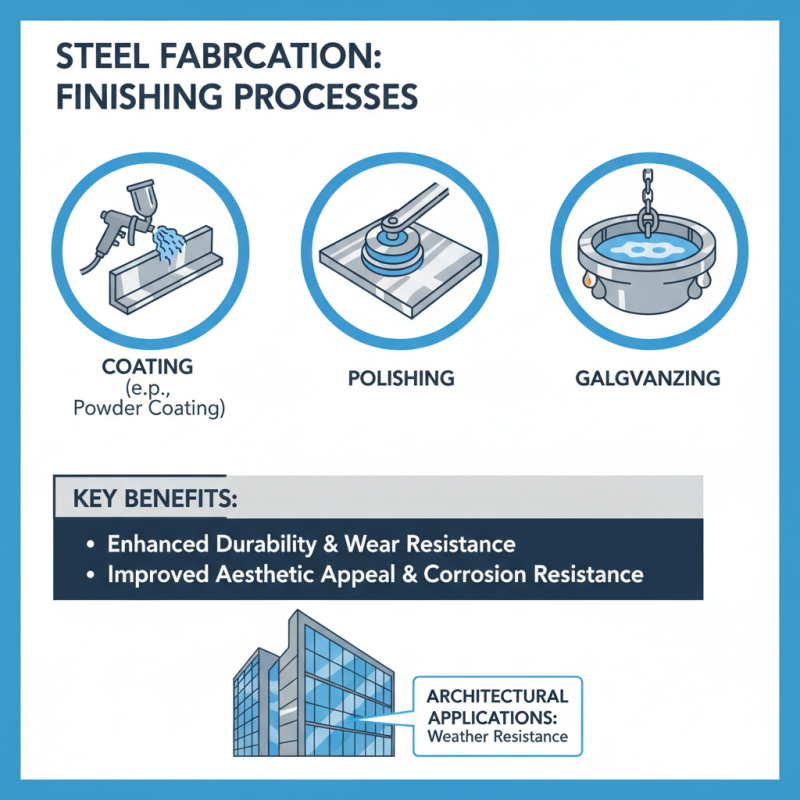
Finishing processes play a crucial role in steel fabrication. They ensure the durability and aesthetic appeal of steel products. Common techniques include coating, polishing, and galvanizing. Each method enhances the steel's resistance to corrosion and wear. For instance, powder coating provides a durable finish that is both appealing and functional. It is often used in architectural applications to improve weather resistance.
Another technique is polishing, which helps achieve a smooth surface. A polished finish can reflect light and can be visually striking. However, it requires precision. Sometimes, the process may not meet the desired standard. This can lead to rework, consuming time and resources. Galvanizing, on the other hand, involves coating the steel with zinc. This process prevents rusting and extends the lifespan of steel components significantly.
Each technique has its challenges. The selection of the right finishing process is essential depending on the intended application. Ignoring this can result in poor performance or reduced durability. Not every approach suits every project, and one must weigh the pros and cons carefully. In steel fabrication, a thoughtful finishing process can make a world of difference.
Steel fabrication plays a crucial role across various industries. In construction, the use of fabricated steel structures has increased by over 60% in the past decade, according to industry reports. Buildings, bridges, and towers utilize steel for strength and durability. This allows for larger spans and innovative designs. In the automotive sector, steel components are essential for vehicle safety and performance. Around 70% of a car's weight typically comes from steel. Its recyclability helps meet sustainability goals.
In the energy industry, steel fabrication is vital for constructing wind turbines and pipelines. As global energy demands rise, the use of fabricated steel in renewable projects is expected to grow by 10% annually. This shift is critical as countries aim for greener energy solutions. Steel's resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for harsh environments like oil rigs.
Tips: When choosing a fabrication partner, prioritize experience and quality. Inspect previous projects for craftsmanship. Communication is key; ensure your needs are understood. Always ask about materials used for sustainability considerations. Regularly review project timelines and budgets to avoid unexpected delays and expenses.